
propylene glycol peak: resonates at 1.N-acetylaspartate (NAA) peak: resonates at 2.0 ppm.glutamine-glutamate peak: resonates at 2.2-2.4 ppm.gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) peak: resonates at 2.2-2.4 ppm.2-hydroxyglutarate peak: resonates at 2.25 ppm.arterial spin labeling (ASL) MR perfusion.dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE) MR perfusion.dynamic susceptibility contrast (DSC) MR perfusion.metal artifact reduction sequence (MARS).
turbo inversion recovery magnitude (TIRM).fluid attenuation inversion recovery (FLAIR).diffusion tensor imaging and fiber tractography.MRI pulse sequences ( basics | abbreviations | parameters).iodinated contrast-induced thyrotoxicosis.iodinated contrast media adverse reactions.clinical applications of dual-energy CT.as low as reasonably achievable (ALARA).TSE technique also reduces the number of interleaved slices that can be obtained.A common technique involves filling the center of K space, which contributes the most to image contrast, using the echoes that have desirable TE the apparent or "effective" TE of the image depends on how the FSE-generated echoes are used to fill K space.This is more pronounced with longer echo train lengths since multiple echoes are acquired per excitation pulse, FSE technique results in varying, progressively increased TE times during each TR acquisition cycle.time to echo (TE) affects the T2 weighting of an image, and is defined as the time interval between excitation pulse and peak echo.Thus, later echoes will be subject to lower SNR echo amplitude decreases as a function of time from excitation pulse.However, the benefit of reduced imaging time comes at a few costs: This minimizes the number of excitation pulse repetitions required per image.īecause echoes are generated using 180-degree inversion pulses, FSE retains the benefit of correcting for external magnetic field inhomogeneity. spinal imaging), and the phase encoding direction is chosen to correspond with the smallest matrix size dimension. The improvement in imaging time is most powerful when used with a rectangular field of view (e.g. Fast spin echo sequenceįSE results in reduced imaging times, with the extent of reduction dependent on the number of echoes produced in each cycle this is also known as the echo train length. In this way, multiple lines of K space (corresponding to multiple phase-encoded steps) are encoded after a single 90-degree pulse.
SPIN ECHO SEQUENCE DIAGRAM SERIES
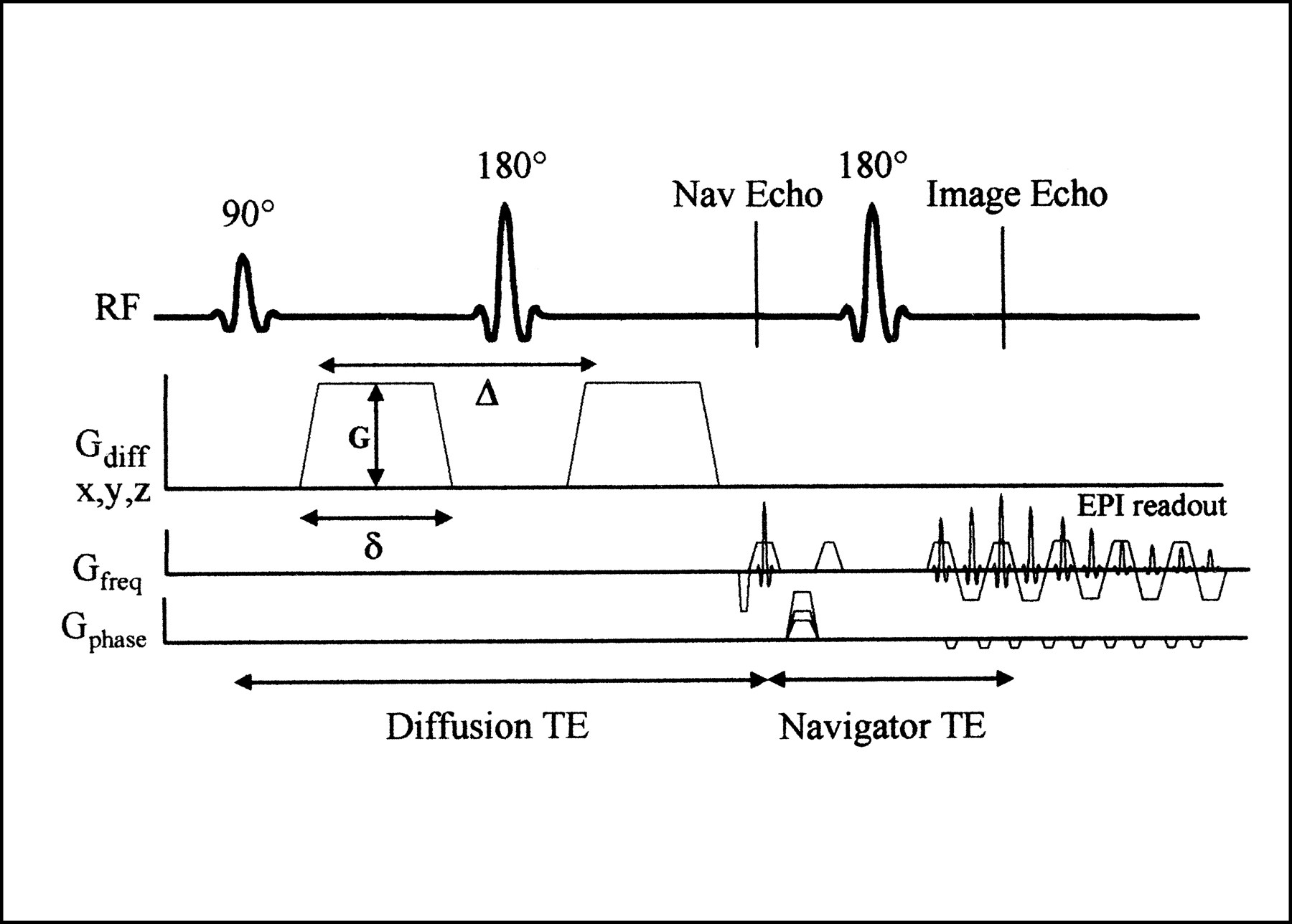
This is achieved by transmitting a series of 180-degree inversion pulses at set intervals and measuring the corresponding echo according to a slightly different phase encoding gradient. FSE In the pulse sequence timing diagram, a fast. 120 ln M / M 0 T E T 2 2 G 2 D 2 / 3 where T E is the echo time, T E / 2 is an interval between the / 2 and rf pulse, D is the diffusion coefficient, and is the duration time of the gradient G. FSE is more efficient because multiple echoes are recorded after each 90-degree excitation pulse (multiple echoes per TR). Timing diagram for the PGSE NMR imaging pulse sequence for determining self-diffusion coefficients. In a basic SE sequence, a single echo is measured during each repetition time (TR). It has largely supplanted the original spin-echo technique due to vastly improved imaging speed.
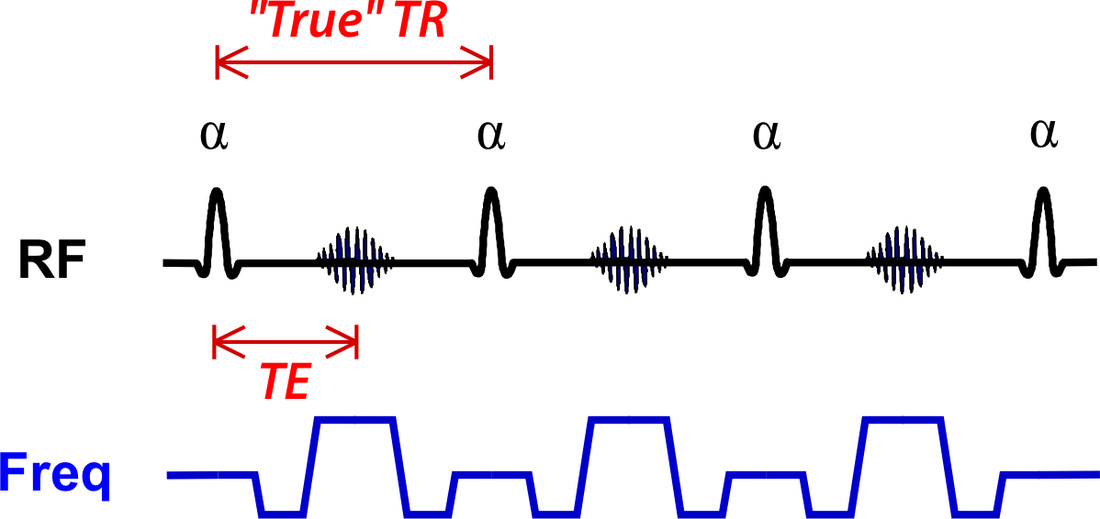
Fast or turbo spin echo ( FSE/ TSE) is an adaptation of conventional spin-echo (SE) acquisition technique designed to reduce imaging time.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
